Innovative Landfill Gas Control and Management

Landfill gas is a natural byproduct of the decomposition of garbage in landfills. Its primary component, methane, is a greenhouse gas 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Municipal solid waste landfills are major emitters of methane, making effective landfill gas collection yet another tool in the strategy to control greenhouse gases.
Langan’s innovative three-dimensional (3D) pneumatic modeling tools are gaining attention in landfill engineering and redevelopment. The use of 3D pneumatic modeling plays an essential role in designing a more effective and cost-efficient methane collection and management system than conventional methods. Langan’s pneumatic models can predict the effects of refuse settlement, seismic activity, proposed development constraints (e.g., piles and other structural elements), and fluctuating landfill gas generation rates and barometric pressures.
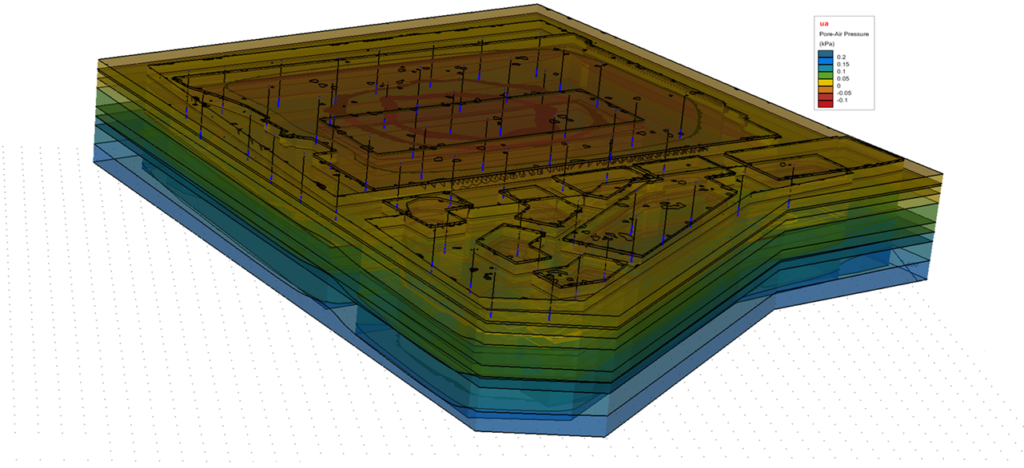
As an example, Langan is providing environmental, geotechnical, and site/civil engineering to develop a 200-acre closed landfill in California. For this project, Langan used a 3D pneumatic model to simulate the performance of the proposed landfill gas collection system under multiple scenarios. Numerous regulatory agencies reviewed the landfill gas collection system design that relied heavily on the computational pneumatic model. The modeling enabled Langan to predict the system performance in the landfill, in three-dimensions, at any point and any given time, to demonstrate that the design will be protective of human health and the environment for the life of the development.
